As a pioneer in steganalysis and steganography forensics, WetStone has a long history of providing tools, services and expertise throughout the world. Our roots in steganography began in the 1990s as participants in funded research and development contracts with the United States Government.
Building upon the expertise we gained in our R&D efforts WetStone began to develop commercial products for use by digital forensic investigators and the law enforcement community. These commercial products include StegoHunt, StegoCommand, Discover the Hidden, as well as their predecessor, StegoSuite.
Our subject matter expertise is highly sought after. WetStone’s elite team of researchers and investigators has participated in steganalysis investigations, published one of the leading books on data hiding, been featured in many journals and magazines, interviewed in the media, and presented at cyber security and digital forensic conferences around the world on the subject of steganography.
Building on over twenty years of ground-breaking research and development, WetStone is dedicated to providing the industry’s most advanced tools and services for steganography detection and analysis.
Steganography Detection and Steganalysis Tools from WetStone

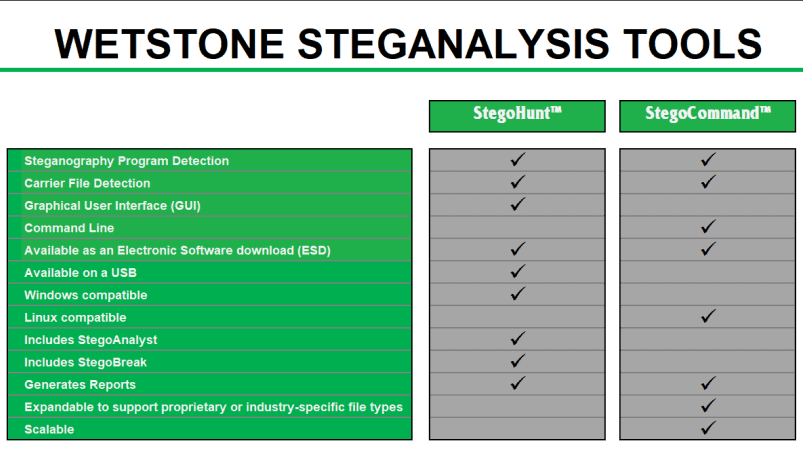
StegoHunt effectively detects the presence of both data hiding programs and the files in which data may have been hidden (carrier files).
Included with StegoHunt:
StegoAnalyst, a steganography analysis tool that provides deep investigation of detected images and audio files.
StegoBreak, a tool used to quickly and easily creak and extract payloads from many carrier files using a simple point and click interface.
StegoCommand is a command line Linux application that scans directories containing files to be examined for the presence of steganography using a collection of detection algorithms.
StegoCommand supports several “out-of-the-box” file types for scanning for the presence of steganography. In addition to the “out-of-the-box” file types offered, the WetStone Technologies research and development team can work directly with a customer to expand the capabilities to scan for steganography in unique, custom, proprietary or industry-specific file types.
StegoCommand is easily deployed in either on-premise or cloud-based environments
Steganography Glossary
Steganography – the practice of concealing a file, message, image, or video within another file, message, image, or video. The word steganography comes from New Latin steganographia, which combines the Greek words steganós, meaning "covered or concealed", and -graphia meaning "writing".
Steganography Malware (Stegware) - the use of steganography by malware to avoid detection. It can be used to penetrate a system, to leak sensitive information and to run a command and control channel without detection.
Steganography Program – Also referred to as Steganography Tool or Steganography Application – computer software that performs some method of data hiding using steganography techniques.
Steganalysis – the process of detecting evidence of hidden data created by a steganography program or steganographic technique
Payload – the data that has been hidden
Carrier – a signal, stream or data file that hides the payload
Suspect files - files considered likely to contain a payload.
Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT) Function – expresses a finite sequence of data points in terms of a sum of cosine functions oscillating at different frequencies. This function is used in many digital media for data compression. Examples of this are JPEG and MPEG
Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT) Coefficient – is the quantized weight applied to each function’s frequency. In Steganalysis, the DCT Coefficients are analyzed to evaluate normal or expected frequencies within the file
Lossy compression – compression method that uses inexact approximations and partial data discarding to represent the content. These techniques are used to reduce data size for storing, handling, and transmitting content. DCT Function is a type of lossy compression.
Lossless compression – compression method that allows the original data to be perfectly reconstructed from the compressed data.
RGB color values – Red, Green and Blue intensities used to define a pixel color in a True Color or Raw digital image. For example 0, 0 ,0 represents the pixel color black and 255, 255, 255 represents the pixel color white. In a palette image the RGB value is represented in a single byte (8 bits). This byte acts as an index to a palette that defines the RGB value.
Color pairs or color buddies - pixel data values that differ only in the least significant bit (LSB), resulting in colors that close in color and at times undetectable to the naked eye. Investigating pixel data values is used in Steganalysis of palette images.
Least significant bit (LSB) Steganography – the least significant bit(LSB) is a binary integer giving the units value, that is, determining whether the number is even or odd. The lsb is sometimes referred to as the right-most bit, due to the convention in positional notation of writing less significant digits further to the right. In steganography flipping(changing its value from a 1 to 0 or o to 1) the LSB is a commonly used technique to hide messages in an image.
Statistical anomaly detection – the method of detecting steganography by identifying or observing data that differs significantly from the majority of the data being analyzed.
Structural anomaly detection - the method of detecting steganography by identifying or observing unexpected data in the structure or attributes of a file
Steganography Program Artifacts – the evidence left behind by the steganography application producing the steganography
Steganography Signatures – identifiable information left inside files after data has been hidden in the file. These signatures are unique to a particular steganography program and help in steganalysis.
Steganographic file system – hiding files or directories with in the storage of a machine that can not be seen without the access key.




